The Versatile Applications of Ceramic Materials in Medical Devices
Introduction:
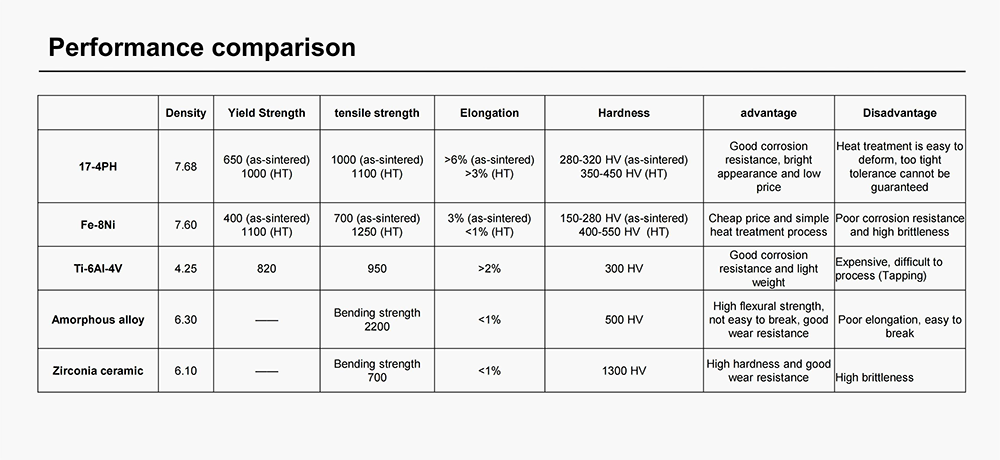
Ceramic materials, often underappreciated in the world of medical devices, possess a wide range of unique properties that make them invaluable in various healthcare applications. While metals and polymers are commonly associated with medical device manufacturing, ceramic materials, including zirconia, silicon nitride, and others, have carved out their niche due to their exceptional attributes. This article explores the versatile applications of ceramic materials in the realm of medical devices.
1. Zirconia Ceramics for Dental Implants:
Zirconia ceramics, known for their excellent biocompatibility and high strength, have found extensive use in the field of dental implants. These ceramics provide a robust and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional materials, ensuring long-lasting and reliable tooth replacements.
2. Silicon Nitride for Orthopedic Implants:
Silicon nitride ceramics are characterized by their outstanding wear resistance, high strength, and biocompatibility. As a result, they are employed in the manufacture of orthopedic implants, such as joint prostheses, bone plates, and screws. These implants offer durability and stability, vital for patients’ mobility and comfort.
3. Ceramic Composite Materials:
Ceramic materials can also be combined with other substances to create composite materials that offer the best of both worlds. For example, combining zirconia ceramics with titanium alloys results in composite implants that exhibit the biocompatibility of zirconia and the strength of titanium.
4. Ceramic Coatings for Enhanced Properties:
Ceramic coatings can be applied to the surfaces of metal medical devices to enhance their wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. This technology is particularly useful for surgical instruments, dental tools, and orthopedic implants, ensuring longevity and performance.
5. Ceramics in Diagnostic Equipment:
Ceramics play a crucial role in diagnostic equipment used in healthcare settings. Ceramic components can be found in X-ray tubes, ultrasound transducers, and electrolyte sensors, contributing to the precision and reliability of medical diagnostics.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, ceramic materials offer a diverse set of advantages that are increasingly being recognized and harnessed in the field of medical devices. Their biocompatibility, wear resistance, high strength, and chemical stability make them suitable for various applications, from dental and orthopedic implants to diagnostic equipment. While ceramics may present challenges related to their inherent brittleness and processing complexity, their unique properties make them a valuable addition to the materials arsenal for medical device manufacturing. As the medical industry continues to evolve, the use of ceramic materials is likely to expand, providing patients with safer, more durable, and effective medical solutions.

